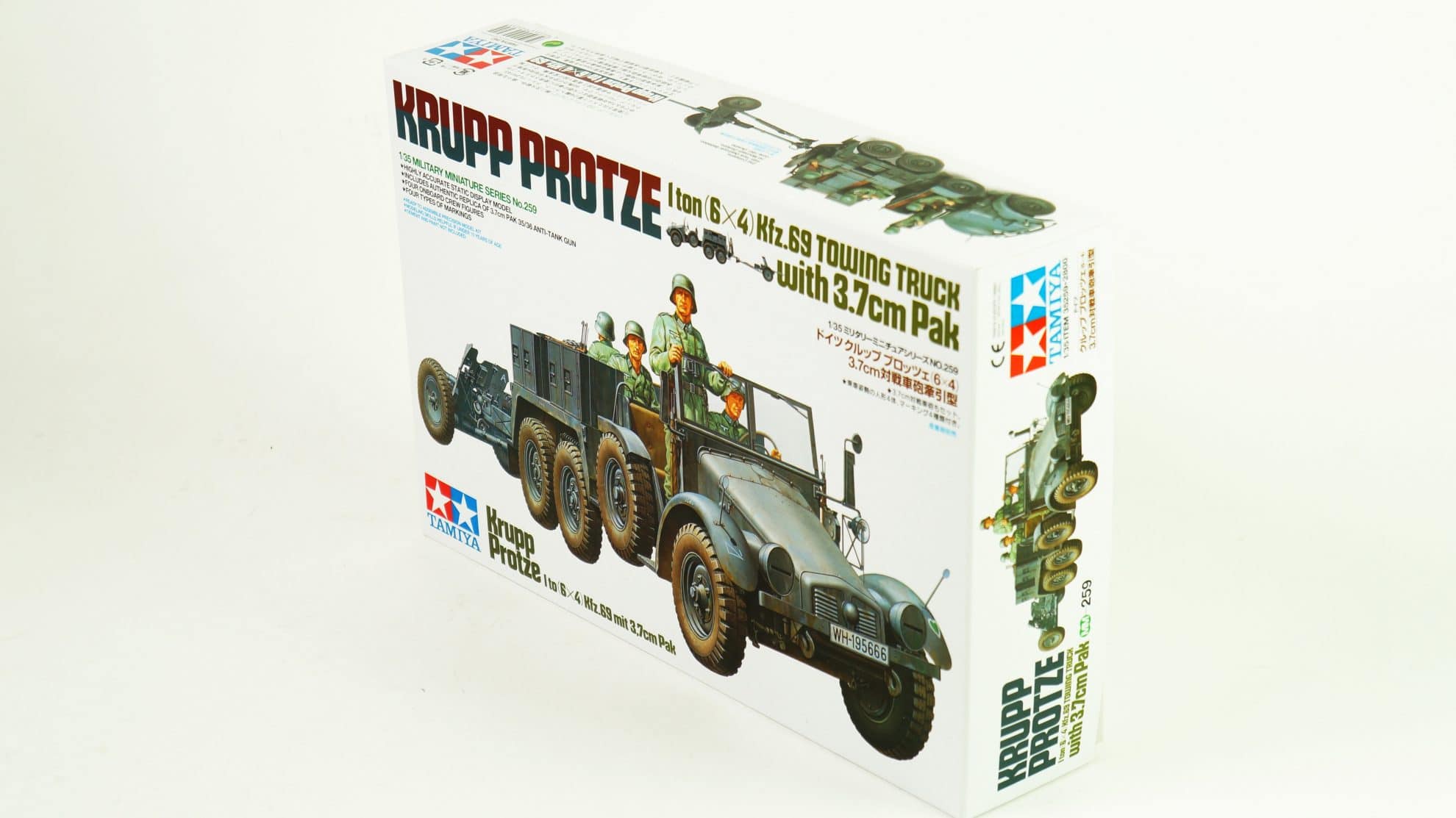
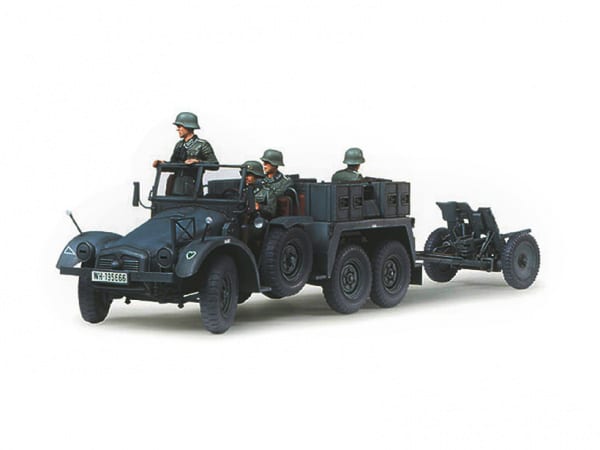
1/35 Krupp Towing Truck w/37mm Pak
33,50€
Only 1 left in stock

*Please check our Privacy Policies to see how to we use your personal data.
*Por favor revisa nuestra Política de Privacidad para ver como tratamos tus datos personales
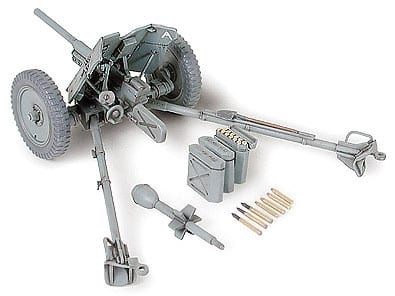
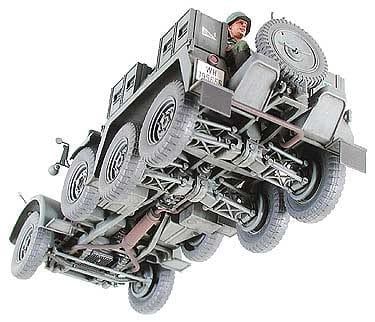
As Germany mobilized its military after Hitler’s seizure of power in 1934, the Wehrmacht’s Weapons Department began transforming civilian vehicles into military vehicles. One light (1.5t and under max. load) truck that was selected was the Krupp Companys L2H43. Popularly known as the “Boxer” because of its air-cooled flat-four square 4-cylinder engine, the L2H43 was massed-produced from 1933. This truck was capable of speeds up to 70km/h. In 1936, this truck had its horsepower improved from 55hp to 60hp with the development of the L2H143 version. This later version underwent various improvements, and various versions such as the personnel transport Kfz.70 were seen. Kfz. numbers were used to designate military transport vehicles (Kfz. 1-30 refer to passenger cars, while Kfz. 31-100 designate trucks). The type refereed to as the Krupp Protze Kfz.69 was designed to tow a 3.7cm PAK 35/36 anti-tank gun and could be fitted with ammunition cases. “Protze” was the German military term used to describe the front-towed carriage was used to carry ammunition and gunner, and would have a cannon hitched to its rear. From the start of WWII, the Krupp Protze Kfz. 69 was employed as standard equipment in anti-tank artillery divisions and was actively deployed to battlefronts in France, Poland, the Balkans, and Russia.
Mientras Alemania movilizaba a sus militares después de la toma del poder por Hitler en 1934, el Departamento de Armas de la Wehrmacht comenzó a transformar los vehículos civiles en vehículos militares. Una camioneta ligera (1.5t y con carga máxima) que fue seleccionada fue la Krupp Companys L2H43. Conocido popularmente como el “Boxer” debido a su motor de cuatro cilindros cuadrados y cuatro cilindros refrigerado por aire, el L2H43 fue producido en masa desde 1933. Este camión era capaz de alcanzar velocidades de hasta 70 km / h. En 1936, este camión mejoró su potencia de 55 hp a 60 hp con el desarrollo de la versión L2H143. Esta última versión sufrió varias mejoras, y se vieron varias versiones como el transporte de personal Kfz.70. Kfz. los números se usaron para designar vehículos de transporte militar (Kfz. 1-30 se refieren a automóviles de pasajeros, mientras que Kfz. 31-100 designan camiones). El tipo designado como Krupp Protze Kfz.69 fue diseñado para remolcar un cañón antitanque PAK 35/36 de 3,7 cm y podría equiparse con cajas de municiones. “Protesta” era el término militar alemán utilizado para describir el carro remolcado por delante que se usaba para transportar municiones y artillero, y tendría un cañón enganchado a su parte trasera. Desde el comienzo de la Segunda Guerra Mundial, el Krupp Protze Kfz. 69 se empleó como equipo estándar en las divisiones de artillería antitanque y se desplegó activamente en frentes de batalla en Francia, Polonia, los Balcanes y Rusia.









 Request of SDS product data file / Product security
Request of SDS product data file / Product security